sett configuration file
sett allows a number of options to be customized via its configuration file. For instance, you may change the default compression level, or define a default data sender.
Depending on your operating system, the default location for the sett configuration file is:
Linux:
~/.config/sett/config.jsonWindows:
C:\Users\%username%\AppData\Roaming\sett\config.jsonMac OS:
~/.config/sett/config.json
Each configuration option has a predefined default value in sett, which is used in case the option is missing from the config file, or if there is no config file. This means that not all configuration options need to be specified in the config file, but only those for which the default value should be overridden.
The sett configuration settings can be modified either by directly editing
the config file, or by using the sett-gui application.
Configuration settings that refer to paths (gpg_home_dir, log_dir)
support the usage of ~ as a shortcut for a user’s home directory in the
path. When sett writes or overwrites a config file, it will automatically
use the ~ shortcut so that the file becomes more easily portable to a
different machine.
Configuration changes using sett-gui
The easiest way to change the sett configuration settings is by using the
Settings tab in sett-gui:
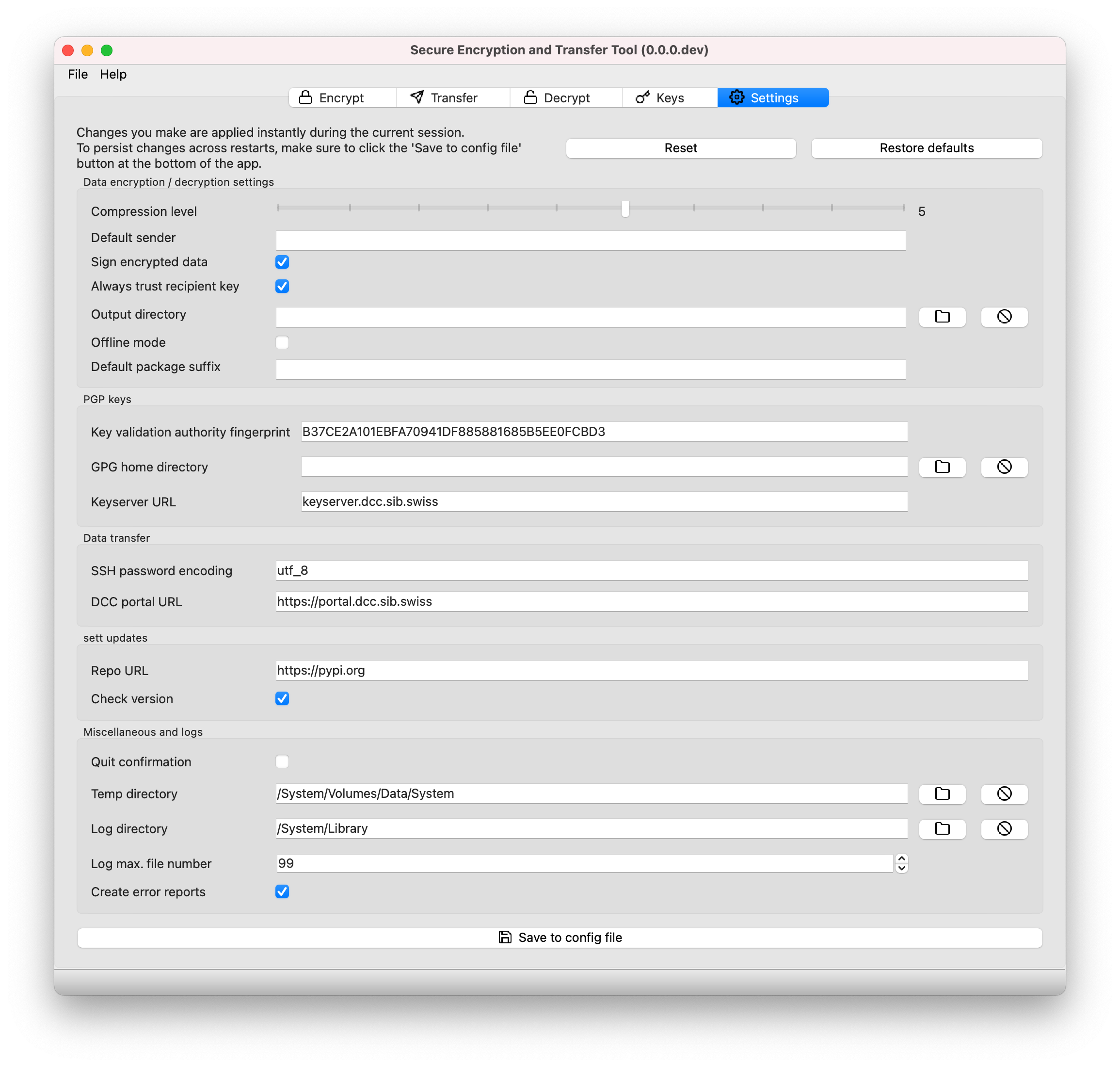
Any change made in the Settings tab becomes effective immediately. However, to make changes persistent (i.e. so that changes are kept even if the application is closed), the Save to config file button at the bottom of the tab must be clicked.
Clicking on Save to config file will write the current settings to the config file, making them persistent across restarts of the application.
Resetting changes made in the Settings tab back to the last persisted settings (i.e. the values in the config file) can be done by clicking on the Reset button.
Settings can also be reset to their factory defaults by using the Restore defaults button, e.g. if you config file has become corrupted.
For detailed settings explanations, please refer to the configuration options section below.
Configuration changes using command line
If no sett configuration file is present on your system, it can be created with:
sett config --create
To display your current configuration settings, the following command can be used. Note that the shown values are the combination of the default values, overridden with the values read from the config file (if a config file exists).
sett config --show
For detailed explanations on the different settings, please refer to the configuration options section below.
Alternative config file location
The SETT_CONFIG_FILE environmental variable allows specifying an alternate
location for the sett configuration file. In the example below, the config
file location is changed to /home/user/custom_sett_config.json:
# Setting a custom config file location for a single command run in a UNIX bash shell.
SETT_CONFIG_FILE=/home/user/custom_sett_config.json sett ...
SETT_CONFIG_FILE=/home/user/custom_sett_config.json sett-gui
# Setting a custom config file location for an entire UNIX bash shell session.
export SETT_CONFIG_FILE=/home/user/custom_sett_config.json
sett ...
sett-gui
# Setting a custom config file location in a Windows PowerShell.
# Note: under Windows there should be no quotes around the variable value.
# E.g. setting SETT_CONFIG_FILE="C:\Users\Alice\sett_config.json" will not work.
set SETT_CONFIG_FILE=C:\Users\Alice\Documents\custom_sett_config.json
sett ...
sett-gui
Configuration options
The following options can be set in the config file:
- always_trust_recipient_key
If
false, the encryption key must be signed by the local user (trueorfalse).- check_version
Check whether you are running the latest version of sett on start-up (
trueorfalse).- compression_level
Default compression level to be used by sett when creating new encrypted data packages (reminder: the data is compressed before it is encrypted). Values must be an integer number in the range 0 (no compression) to 9 (maximum compression). Higher compression levels require more computing time.
- connections
List of predefined connections for data transfer. Example:
"connections": { "sftp@localhost": { "parameters": { "destination_dir": "upload", "host": "localhost", "pkey": "~/.ssh/sftp_ssh_testkey", "username": "sftp" }, "protocol": "sftp" } }
- dcc_portal_url
URL of a BioMedIT portal instance. The portal is used for key approval and DTR (Data Transfer Request) validation.
- default_sender
Default sender fingerprint for encryption.
- gpg_home_dir
Path of the directory where GnuPG stores its keyrings and other configuration settings.
- gui_quit_confirmation
Ask for confirmation to quit sett-gui (
trueorfalse). This option only applies to GUI and does not affect CLI.- gpg_key_autodownload
Allow the automatic download and refresh of PGP keys from the keyserver (
trueorfalse). Iftrue(default value), PGP keys used during encryption/decryption are attempted to be refreshed from the keyserver before they are used (provided a value forkeyserver_urlis given).- keyserver_url
URL of the keyserver: used for publishing/fetching public PGP keys.
- legacy_mode
When enabled, sett reverts to using GnuPG as cryptographic backend instead of the Sequoia library. In legacy mode, sett will also look for PGP keys in the GnuPG keyring, instead of its own certificate store.
- log_dir
Path to log files directory. By default, the log files are saved at the following locations (
~indicates the user’s home directory):Linux:
~/.local/var/log/settMac OS:
~/.local/var/log/settWindows:
~\AppData\Roaming\sett
- log_max_file_number
Maximum number of log files to keep as backup.
- max_cpu
Maximum number of CPU cores for parallel computation. Use
0(default) if you want to use all available CPU cores. Note, only some parts of the encryption and decryption workflows can parallelize computation.- output_dir
Default output directory, relevant for encryption/decryption. This option only applies to sett-gui. In command line, the output location can be specified via the optional argument
--output(resp.-o) for encryption and--output-dir(resp.-o) for decryption.- package_name_suffix
Default suffix for encrypted package name. This option applies to both, sett-gui and the command line. In command line it is possible to override the default suffix with the optional argument
--output-suffix.- repo_url
Python package repository, used when looking for sett updates.
- sftp_buffer_size
Size of buffer in bytes when transferring data with the SFTP protocol (default: 1048576 bytes = 1 Megabyte). This is the size of every packet sent over the network. Larger buffer sizes theoretically result in faster transfer speeds on stable networks but will decrease transfer speed on poor networks (networks with higher probability of packet losses). The default value is on the optimistic side, you might need to be decrease it if transferring data on poor quality networks.
- ssh_password_encoding
Character encoding used for the SSH key password. By default the encoding is assumed to be
utf_8. See the SSH private key with non-ASCII characters section of this guide for further details.- verify_dtr
Verify that the given Data Transfer Request (DTR) ID is valid and the associated metadata is correct, i.e.
DTR ID is valid and the transfer is authorized.
Sender and Recipients public PGP keys are approved by the BioMedIT key validation authority.
Recipients are approved Data Managers of the BioMedIT project for which data is being encrypted.
When Verify DTR is enabled, the project code of the project to which the DTR belongs will be added as a prefix to the output file name.
- verify_key_approval
Verify that a PGP key has been approved by the central authority.
- verify_package_name
If
true(the default), the name of data packages files (i.e. the encrypted files) are verified to match the pattern<project_code>_<date_format>_<package_name_suffix>.zipbefore they are transferred. This is to verify that no sensitive information has been mistakenly included in the file name. This check can be permanently turned-off by changing the value of the setting tofalse, or by un-checking the corresponding checkbox in the Settings tab of sett-gui.